Leveraging Amazon Nova for Multimodal Video Analysis
How to use Amazon Nova for video analysis, object detection with bounding boxes, and content annotation. Includes TypeScript examples for S3 and local video processing with the AWS Bedrock SDK.
Leveraging Amazon Nova for Multimodal Video Analysis
Amazon Nova is a generative AI service on AWS Bedrock that enables developers to build intelligent video analysis applications -- from content annotation and object detection to automated video summarization. This guide walks through Amazon Nova's multimodal capabilities with production-ready TypeScript examples for processing both local and S3-hosted videos, including bounding box object detection.
Key Takeaways
- Amazon Nova processes video through the AWS Bedrock runtime, supporting both local files (up to 25MB base64) and S3-hosted videos (up to 1GB) across formats like MP4, MKV, MOV, and WebM.
- Object detection with bounding boxes is one of Nova's most powerful features, enabling applications in content moderation, accessibility, and interactive video experiences.
- TypeScript integration uses the `@aws-sdk/client-bedrock-runtime` package with `InvokeModelCommand`, and this guide provides the TypeScript examples missing from official documentation.
- Exponential backoff with jitter is essential for handling API throttling when processing multiple videos or frames at scale.
- Real-world applications span content moderation, intelligent video search, accessibility features, security surveillance, and automated content summarization.
Understanding Amazon Nova's Multimodal Capabilities
Amazon Nova is Amazon's generative AI service specifically designed for multimodal content analysis, with robust capabilities for processing video data. Nova can:
- Extract semantic understanding from video content
- Identify objects, actions, and scenes in videos
- Generate detailed descriptions of video content
- Process videos stored both locally and in AWS S3 buckets
- Support object detection with bounding box annotations
- Work across multiple languages (including Mandarin and English)
These capabilities make Nova an ideal choice for applications requiring deep video analysis, content moderation, accessibility features, and automated content summarization.
Getting Started with Amazon Nova
Prerequisites
Before diving into implementation, ensure you have:
- An AWS account with access to the Nova service
- AWS credentials configured on your machine
- Node.js installed (for TypeScript/JavaScript implementations)
- Basic familiarity with AWS SDK
Full fledged TypeScript examples are available in the GitHub repository.
Setting Up Your Environment
First, install the necessary dependencies for working with Nova:
Refer to the package.json below for the dependencies:
You'll also need to set up your AWS credentials either via environment variables or AWS CLI configuration.
Processing Videos with Amazon Nova
Processing Videos Stored in S3
One of the most common use cases is analyzing videos stored in S3 buckets. One of the core difference between processing local videos and S3 videos is the limitation of video size. For local videos, the maximum size is 25MB, while for S3 videos, the maximum size is 1GB. Here's a code snippet for example, only the relevant code is shown.
Processing Local Videos
For development and testing, you might want to process videos stored locally, you can check the core difference in the request schema is the "source" field. For local videos, the "source" field is "bytes" and for S3 videos, the "source" field is "s3Location" with "bucketOwner" field.
You may see similar response (Results: ) as the one below, with necessary logs for debugging:
Advanced Use Case: Object Detection with Bounding Boxes
One of Nova's most powerful features is its ability to detect objects in videos and provide bounding box coordinates. This can be used for applications like content moderation, accessibility, or interactive video experiences.
The following example demonstrates how to specify the prompt for object detection and process the image with the Nova API using retry logic.
Check the sample images below with bounding boxes detected:
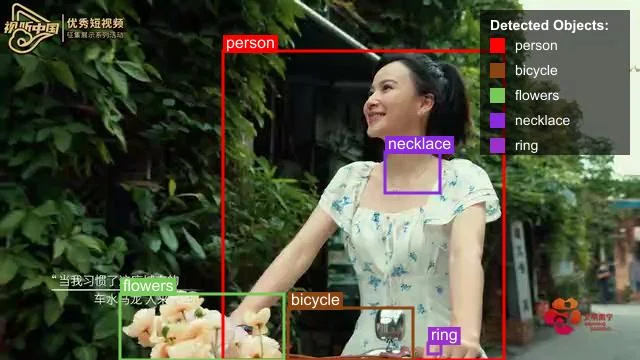
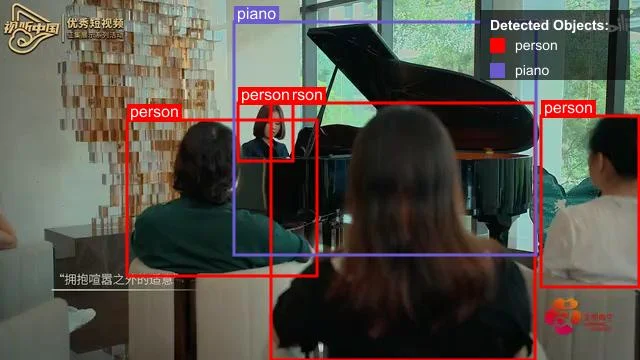

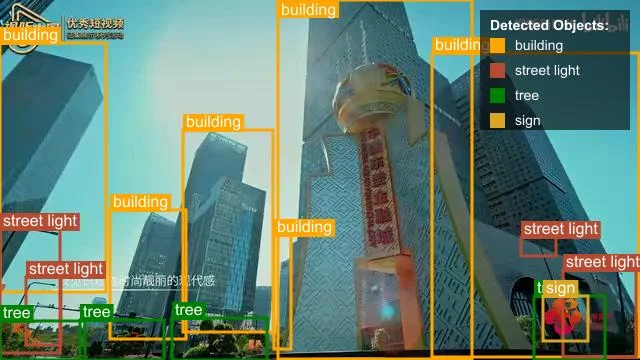

Best Practices for Working with Amazon Nova
Based on the examples and documentation, here are some best practices to follow when working with Nova:
1. Optimize Video Files
- Keep videos under 25MB when using base64 encoding (local videos)
- For larger videos, use S3 URIs which support up to 1GB
- Consider preprocessing videos to reduce file size
2. Craft Effective Prompts
- Be specific about what information you want from the video
- For object detection, clearly specify the expected response format
- Use system messages to guide the model's behavior
3. Handle API Throttling
Implement exponential backoff with jitter for API calls:
4. Monitor Token Usage
Nova's pricing is based on token usage. Monitor and log token consumption:
Real-World Applications
Amazon Nova's video analysis capabilities can be applied in various domains:
- Content Moderation, Automatically detect and flag inappropriate content in user-generated videos.
- Intelligent Video Search, Index videos based on their content, making them searchable by objects, actions, or descriptions.
- Accessibility, Generate detailed video descriptions for visually impaired users.
- Content Summarization, Create concise summaries of long videos for quick consumption.
- Security and Surveillance, Identify unusual activities or specific objects in surveillance footage.
Conclusion
Amazon Nova represents a significant advancement in multimodal AI capabilities, particularly for video analysis. By providing developers with powerful tools to extract meaning from video content, Nova enables a wide range of applications that were previously challenging to implement.
As multimodal AI continues to evolve, services like Nova will become increasingly important for developers looking to build sophisticated applications that can understand and process visual content. By following the guidelines and best practices outlined in this article, you can effectively leverage Nova's capabilities to enhance your applications with intelligent video analysis.
Resources
About the Author
Aaron is a senior software engineer and AI researcher specializing in generative AI, multimodal systems, and cloud-native AI infrastructure. He writes about cutting-edge AI developments, practical tutorials, and deep technical analysis at fp8.co.
Cite this Article
Related Articles
Multimodal Video Search: 10+ Tools Compared (2025)
Compare commercial and open-source multimodal video search platforms. Discover which tools support text, image, and voice queries for precise scene retrieval.
Multimodal AI, Video SearchDeepSeek Multimodal Models: VL, Janus & JanusFlow Explained
Explore DeepSeek AI multimodal models from DeepSeek-VL to Janus and JanusFlow. Learn how each architecture advances vision-language understanding and generation.
Multimodal AI, DeepSeek